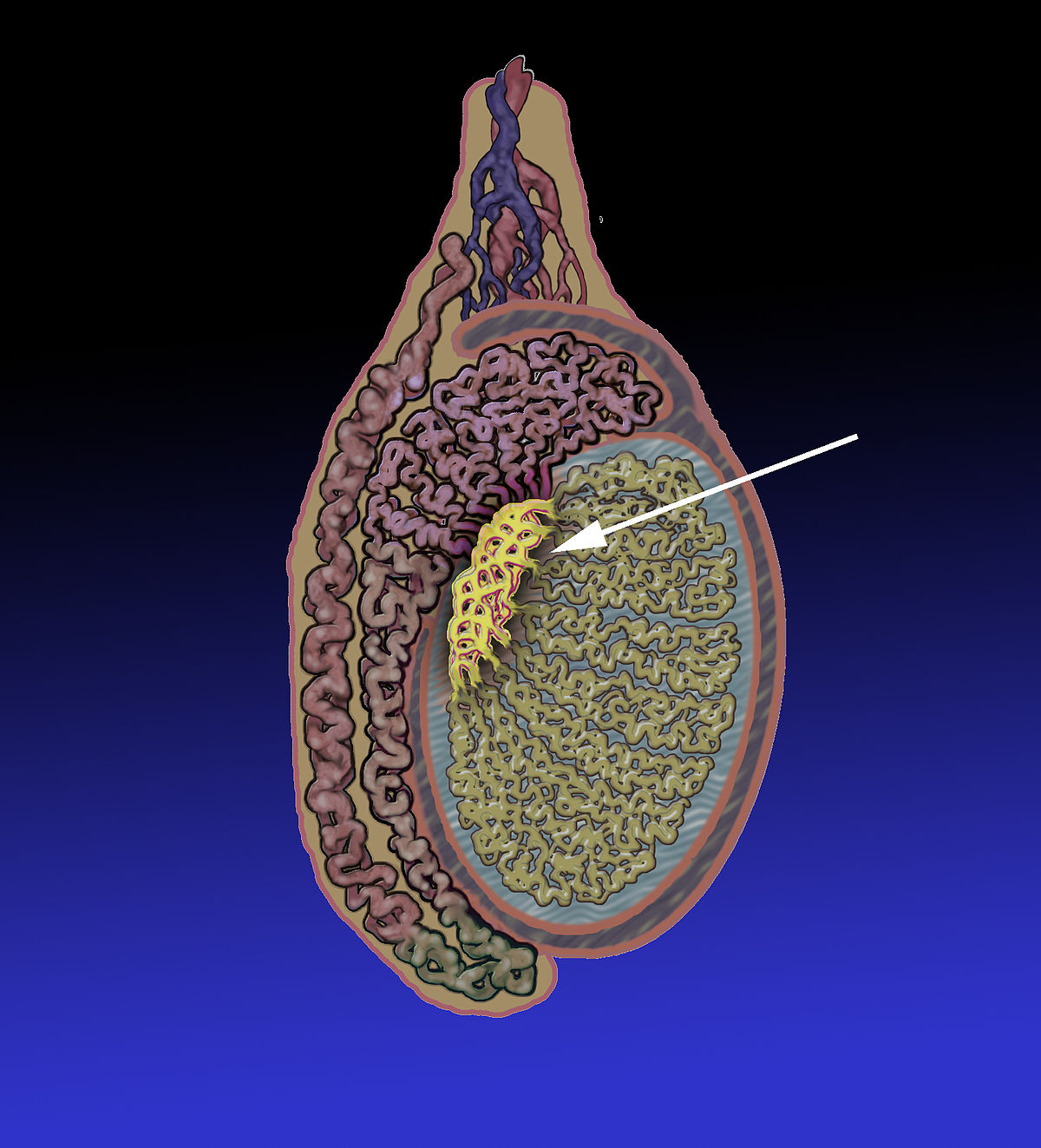
What is Epididymitis?
It is the inflammation of the epididymis, a tubular structure located at the back of the testicles which stores and transports sperm from the testicle to the seminal vesicles.
Symptoms
Epididymitis can be either acute, meaning it lasts for six weeks or less, or chronic, which lasts for six weeks or more. Symptoms for acute epididymitis often come on quickly and may be associated with sudden inflammation, swelling and pain. Acute epididymitis may also include inflammation of the teste.
Chronic epididymitis develops more slowly and is typically accompanied by a dull, achy pain.
Symptoms to watch out for include low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, urgent or frequent urination, abnormal discharge from the penis, or blood in the semen.
Epididymitis is also typically accompanied by pain and/or pressure in the pelvic area and testicles during sexual intercourse, urination or bowel movements. Also watch out for redness, tenderness or warmth in the scrotum.